Information systems differ in their business needs. Also depending upon different levels in organization information systems differ. The major information systems are
-
Transaction processing systems
-
Management information systems
-
Decision support systems
-
Executive Support Systems
-
Expert Support Systems
The picture below shows relation of information system to the levels of organization. The information needs are different at different organizational levels. Accordingly the information can be categorized as: strategic information, managerial information and operational information.

Strategic information is the information needed by top most management for decision making. For example the trends in revenues earned by the organization are required by the top management for setting the policies of the organization. This information is not required by the lower levels in the organization. The information systems that provide these kinds of information are known as Decision Support Systems.
The second category of information required by the middle management is known as managerial information. The information required at this level is used for making short term decisions and plans for the organization. Information like sales analysis for the past quarter or yearly production details etc. fall under this category. Management information system (MIS) caters to such information needs of the organization. Due to its capabilities to fulfill the managerial information needs of the organization, Management Information Systems have become a necessity for all big organizations. And due to its vastness, most of the big organizations have separate MIS departments to look into the related issues and proper functioning of the system.
The third category of information is relating to the daily or short term information needs of the organization such as attendance records of the employees. This kind of information is required at the operational level for carrying out the day-to-day operational activities. Due to its capabilities to provide information for processing transaction of the organization, the information system is known as Transaction Processing System or Data Processing System. Some examples of information provided by such systems are processing of orders, posting of entries in bank, evaluating overdue purchaser orders etc..
Transaction Processing Systems
 | 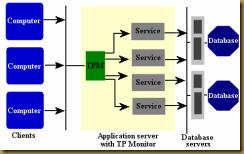 |
TPS processes business transaction of the organization. Transaction can be any activity of the organization. Transactions differ from organization to organization. For example, take a railway reservation system. Booking, canceling, etc. are all transactions. Any query made to it is a transaction. However, there are some transactions, which are common to almost all organizations. Like employee new employee, maintaining their leave status, maintaining employees accounts, etc.
This provides high speed and accurate processing of record keeping of basic operational processes. These include calculation, storage and retrieval.
Transaction processing systems provide speed and accuracy, and can be programmed to follow routines functions of the organization.
Management Information Systems
 |  |
These systems assist lower management in problem solving and making decisions. They use the results of transaction processing and some other information also. It is a set of information processing functions. It should handle queries as quickly as they arrive. An important element of MIS is database.
A database is a non-redundant collection of interrelated data items that can be processed through application programs and available to many users.
Decision Support Systems
 |  |
These systems assist higher management to make long term decisions. These type of systems handle unstructured or semi structured decisions. A decision is considered unstructured if there are no clear procedures for making the decision and if not all the factors to be considered in the decision can be readily identified in advance.
These are not of recurring nature. Some recur infrequently or occur only once. A decision support system must very flexible. The user should be able to produce customized reports by giving particular data and format specific to particular situations.
Executive Support System
 |  |
Executive Support System (ESS) is a reporting tool (software) that allows you to turn your organization's data into useful summarized reports. These reports are generally used by executive level managers for quick access to reports coming from all company levels and departments such as billing, cost accounting , staffing, scheduling, and more.
In addition to providing quick access to organized data from departments, some Executive Support System tools also provide analysis tools that predicts a series of performance outcomes over time using the input data. This type of ESS is useful to executives as it provides possible outcomes and quick reference to statistics and numbers needed for decision-making.
Expert Support System
 |  |
It is a computer system or program that uses artificial intelligence techniques to solve problems that ordinarily require a knowledgeable human. The method used to construct such systems, knowledge engineering, extracts a set of rules and data from an expert or experts through extensive questioning. This material is then organized in a format suitable for representation in a computer and a set of tools for inquiry, manipulation, and response is applied. While such systems do not often replace the human experts, they can serve as useful adjuncts or assistants. Among some of the successful expert systems developed are internist, a medical diagnosis tool that contains nearly 100,000 relationships between symptoms and diseases, and prospector, an aid to geologists in interpreting mineral data.
No comments:
Post a Comment